Revelle (1979) proposed that hierachical cluster analysis could be used to estimate a new coefficient (beta) that was an estimate of the general factor saturation of a test. More recently, Zinbarg, Revelle, Yovel and Li (2005) compared McDonald's Omega to Chronbach's alpha and Revelle's beta. They conclude that omega is the best estimate. An algorithm for estimating omega using R is available as part of the "psych" package at http://personality-project.org/r.
Although ICLUST was originally written in FORTRAN for a CDC 6400 and then converted for IBM mainframes, Cooksey and Soutar, (2005) report using a PC adaptation of the original FORTRAN program. A modified version, written in Lightspeed Pascal has been available for the Mac for several years but did not have all the graphic features of the original program.
I now release a completely new version of ICLUST, written in R. It is still under development but is included as part of the "psych" package. Although early testing suggests it is stable, let me know if you have problems. Please email me if you want help with this version of ICLUST or if you desire more features.
The program currently has three primary functions: cluster, loadings, and graphics. There is no documentation yet for the program, although one can figure out most requirements by reading the code.
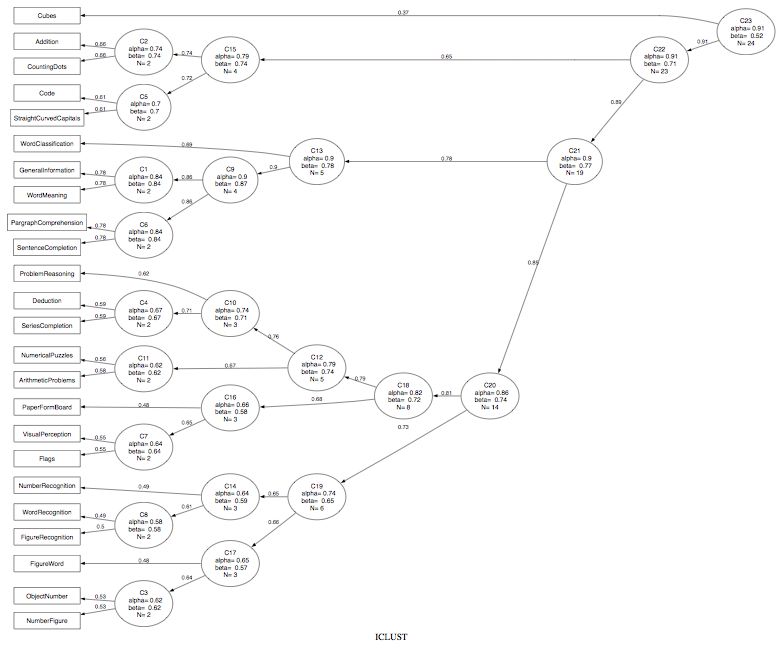
A sample output using the 24 variable problem by Harman can be represented both graphically and in terms of the cluster order. Note that the graphic is created using GraphViz in the dot language. ICLUST.graph produces the dot code for Graphviz. I have also tried doing this in Rgraphviz with less than wonderful results. Dot code can be viewed directly in Graphviz or can be tweaked using commercial software packages (e.g., OmniGraffle)

Note that for this problem, with these parameters, the data formed one large cluster. (This is consistent with the Very Simple Structure (VSS) output as well, which shows a clear one factor solution for complexity 1 data.) See below for an example with this same data set, but with more stringent parameter settings.
r.mat<- Harman74.cor$cov
iq.clus <- ICLUST(r.mat)
ICLUST.graph(iq.clus,title="ICLUST of 24 mental variables",out.file="iclust.dot")
$title
[1] "ICLUST"
$clusters
VisualPerception Cubes PaperFormBoard Flags GeneralInformation PargraphComprehension
1 1 1 1 1 1
SentenceCompletion WordClassification WordMeaning Addition Code CountingDots
1 1 1 1 1 1
StraightCurvedCapitals WordRecognition NumberRecognition FigureRecognition ObjectNumber NumberFigure
1 1 1 1 1 1
FigureWord Deduction NumericalPuzzles ProblemReasoning SeriesCompletion ArithmeticProblems
1 1 1 1 1 1
$corrected
[,1]
[1,] 1
$loadings
[,1]
VisualPerception 0.55
Cubes 0.34
PaperFormBoard 0.38
Flags 0.44
GeneralInformation 0.60
PargraphComprehension 0.59
SentenceCompletion 0.57
WordClassification 0.60
WordMeaning 0.59
Addition 0.41
Code 0.51
CountingDots 0.43
StraightCurvedCapitals 0.55
WordRecognition 0.39
NumberRecognition 0.37
FigureRecognition 0.48
ObjectNumber 0.44
NumberFigure 0.49
FigureWord 0.42
Deduction 0.56
NumericalPuzzles 0.55
ProblemReasoning 0.56
SeriesCompletion 0.63
ArithmeticProblems 0.60
$fit
$fit$clusterfit
[1] 0.76
$fit$factorfit
[1] 0.76
$results
Item/Cluster Item/Cluster similarity correlation alpha1 alpha2 beta1 beta2 size1 size2 rbar1 rbar2 r1 r2 alpha beta rbar size
C1 V9 V5 1.00 0.72 0.72 0.72 0.72 0.72 1 1 0.72 0.72 0.78 0.78 0.84 0.84 0.72 2
C2 V12 V10 1.00 0.58 0.58 0.58 0.58 0.58 1 1 0.58 0.58 0.66 0.66 0.74 0.74 0.58 2
C3 V18 V17 1.00 0.45 0.45 0.45 0.45 0.45 1 1 0.45 0.45 0.53 0.53 0.62 0.62 0.45 2
C4 V23 V20 1.00 0.51 0.51 0.51 0.51 0.51 1 1 0.51 0.51 0.59 0.59 0.67 0.67 0.51 2
C5 V13 V11 1.00 0.54 0.54 0.54 0.54 0.54 1 1 0.54 0.54 0.61 0.61 0.70 0.70 0.54 2
C6 V7 V6 1.00 0.72 0.72 0.72 0.72 0.72 1 1 0.72 0.72 0.78 0.78 0.84 0.84 0.72 2
C7 V4 V1 0.98 0.47 0.47 0.48 0.47 0.48 1 1 0.47 0.48 0.55 0.55 0.64 0.64 0.47 2
C8 V16 V14 0.98 0.41 0.43 0.41 0.43 0.41 1 1 0.43 0.41 0.50 0.49 0.58 0.58 0.41 2
C9 C1 C6 0.93 0.78 0.84 0.84 0.84 0.84 2 2 0.72 0.72 0.86 0.86 0.90 0.87 0.69 4
C10 C4 V22 0.91 0.56 0.67 0.56 0.67 0.56 2 1 0.51 0.56 0.71 0.62 0.74 0.71 0.49 3
C11 V21 V24 0.86 0.45 0.51 0.53 0.51 0.53 1 1 0.51 0.53 0.56 0.58 0.62 0.62 0.45 2
C12 C10 C11 0.86 0.58 0.74 0.62 0.71 0.62 3 2 0.49 0.45 0.76 0.67 0.79 0.74 0.43 5
C13 C9 V8 0.85 0.64 0.90 0.64 0.87 0.64 4 1 0.69 0.64 0.90 0.69 0.90 0.78 0.64 5
C14 C8 V15 0.84 0.41 0.58 0.41 0.58 0.41 2 1 0.41 0.41 0.61 0.49 0.64 0.59 0.37 3
C15 C2 C5 0.82 0.59 0.74 0.70 0.74 0.70 2 2 0.58 0.54 0.74 0.72 0.79 0.74 0.49 4
C16 V3 C7 0.81 0.41 0.41 0.64 0.41 0.64 1 2 0.41 0.47 0.48 0.65 0.66 0.58 0.39 3
C17 V19 C3 0.80 0.40 0.41 0.62 0.41 0.62 1 2 0.41 0.45 0.48 0.64 0.65 0.57 0.38 3
C18 C12 C16 0.78 0.57 0.79 0.66 0.74 0.58 5 3 0.43 0.39 0.79 0.68 0.82 0.72 0.37 8
C19 C17 C14 0.76 0.49 0.64 0.64 0.57 0.59 3 3 0.38 0.37 0.66 0.65 0.74 0.65 0.32 6
C20 C18 C19 0.76 0.59 0.82 0.74 0.72 0.65 8 6 0.37 0.32 0.81 0.73 0.86 0.74 0.30 14
C21 C20 C13 0.71 0.62 0.86 0.90 0.74 0.78 14 5 0.30 0.64 0.85 0.78 0.90 0.77 0.32 19
C22 C15 C21 0.65 0.55 0.79 0.90 0.74 0.77 4 19 0.49 0.32 0.65 0.89 0.91 0.71 0.31 23
C23 C22 V2 0.62 0.35 0.91 0.35 0.71 0.35 23 1 0.31 0.35 0.91 0.37 0.91 0.52 0.30 24
$cor
[,1]
[1,] 1
$alpha
[1] 0.91
$size
[1] 24
Graphviz (or OmniGraffle) can open the dot file (ICLUST.dot) and will show the figure. (See above). The dot file can be edited with a normal text editor to make the figure cleaner.
The previous solution showed that all 24 mental tests formed one, high level cluster (g). An alternative is to form smaller, tighter clusters. These were formed, of course, in the previous analysis, but it would be nice to find the correlations, loadings, and fit statistics for a multiple cluster solution.
Note that the cluster fit, and the more stringent factor fit are worse for this solution than the previous solution. Also note that one of the "clusters" is a single variable (cubes).
r.mat<- Harman74.cor$cov
iq.clus <- ICLUST(r.mat,nclusters=4)
graph.out <- file.choose()
ICLUST.graph(iq.clus,graph.out,title = "ICLUST of 24 mental variables")
iq.clus
$title
[1] "ICLUST"
$clusters
V2 C13 C15 C20
VisualPerception 0 0 0 1
Cubes 1 0 0 0
PaperFormBoard 0 0 0 1
Flags 0 0 0 1
GeneralInformation 0 1 0 0
PargraphComprehension 0 1 0 0
SentenceCompletion 0 1 0 0
WordClassification 0 1 0 0
WordMeaning 0 1 0 0
Addition 0 0 1 0
Code 0 0 1 0
CountingDots 0 0 1 0
StraightCurvedCapitals 0 0 1 0
WordRecognition 0 0 0 1
NumberRecognition 0 0 0 1
FigureRecognition 0 0 0 1
ObjectNumber 0 0 0 1
NumberFigure 0 0 0 1
FigureWord 0 0 0 1
Deduction 0 0 0 1
NumericalPuzzles 0 0 0 1
ProblemReasoning 0 0 0 1
SeriesCompletion 0 0 0 1
ArithmeticProblems 0 0 0 1
$corrected
V2 C13 C15 C20
V2 1.00 0.26 0.21 0.41
C13 0.24 0.90 0.47 0.71
C15 0.19 0.40 0.79 0.67
C20 0.38 0.62 0.55 0.86
$loadings
V2 C13 C15 C20
VisualPerception 0.32 0.38 0.39 0.57
Cubes 1.00 0.24 0.19 0.38
PaperFormBoard 0.32 0.31 0.15 0.42
Flags 0.23 0.38 0.22 0.45
GeneralInformation 0.28 0.77 0.39 0.50
PargraphComprehension 0.23 0.77 0.31 0.53
SentenceCompletion 0.16 0.80 0.32 0.49
WordClassification 0.16 0.67 0.40 0.56
WordMeaning 0.20 0.79 0.27 0.54
Addition 0.06 0.29 0.63 0.35
Code 0.15 0.36 0.61 0.48
CountingDots 0.14 0.21 0.65 0.40
StraightCurvedCapitals 0.24 0.40 0.62 0.51
WordRecognition 0.10 0.31 0.27 0.41
NumberRecognition 0.13 0.26 0.22 0.41
FigureRecognition 0.27 0.28 0.27 0.56
ObjectNumber 0.00 0.29 0.36 0.47
NumberFigure 0.26 0.25 0.43 0.54
FigureWord 0.11 0.29 0.27 0.46
Deduction 0.29 0.51 0.27 0.58
NumericalPuzzles 0.31 0.36 0.50 0.54
ProblemReasoning 0.23 0.49 0.30 0.58
SeriesCompletion 0.35 0.54 0.40 0.62
ArithmeticProblems 0.21 0.50 0.54 0.54
$fit
$fit$clusterfit
[1] 0.51
$fit$factorfit
[1] 0.16
$results
Item/Cluster Item/Cluster similarity correlation alpha1 alpha2 beta1 beta2 size1 size2 rbar1 rbar2 r1 r2 alpha beta rbar size
C1 V9 V5 1.00 0.72 0.72 0.72 0.72 0.72 1 1 0.72 0.72 0.78 0.78 0.84 0.84 0.72 2
C2 V12 V10 1.00 0.58 0.58 0.58 0.58 0.58 1 1 0.58 0.58 0.66 0.66 0.74 0.74 0.58 2
C3 V18 V17 1.00 0.45 0.45 0.45 0.45 0.45 1 1 0.45 0.45 0.53 0.53 0.62 0.62 0.45 2
C4 V23 V20 1.00 0.51 0.51 0.51 0.51 0.51 1 1 0.51 0.51 0.59 0.59 0.67 0.67 0.51 2
C5 V13 V11 1.00 0.54 0.54 0.54 0.54 0.54 1 1 0.54 0.54 0.61 0.61 0.70 0.70 0.54 2
C6 V7 V6 1.00 0.72 0.72 0.72 0.72 0.72 1 1 0.72 0.72 0.78 0.78 0.84 0.84 0.72 2
C7 V4 V1 0.98 0.47 0.47 0.48 0.47 0.48 1 1 0.47 0.48 0.55 0.55 0.64 0.64 0.47 2
C8 V16 V14 0.98 0.41 0.43 0.41 0.43 0.41 1 1 0.43 0.41 0.50 0.49 0.58 0.58 0.41 2
C9 C1 C6 0.93 0.78 0.84 0.84 0.84 0.84 2 2 0.72 0.72 0.86 0.86 0.90 0.87 0.69 4
C10 C4 V22 0.91 0.56 0.67 0.56 0.67 0.56 2 1 0.51 0.56 0.71 0.62 0.74 0.71 0.49 3
C11 V21 V24 0.86 0.45 0.51 0.53 0.51 0.53 1 1 0.51 0.53 0.56 0.58 0.62 0.62 0.45 2
C12 C10 C11 0.86 0.58 0.74 0.62 0.71 0.62 3 2 0.49 0.45 0.76 0.67 0.79 0.74 0.43 5
C13 C9 V8 0.85 0.64 0.90 0.64 0.87 0.64 4 1 0.69 0.64 0.90 0.69 0.90 0.78 0.64 5
C14 C8 V15 0.84 0.41 0.58 0.41 0.58 0.41 2 1 0.41 0.41 0.61 0.49 0.64 0.59 0.37 3
C15 C2 C5 0.82 0.59 0.74 0.70 0.74 0.70 2 2 0.58 0.54 0.74 0.72 0.79 0.74 0.49 4
C16 V3 C7 0.81 0.41 0.41 0.64 0.41 0.64 1 2 0.41 0.47 0.48 0.65 0.66 0.58 0.39 3
C17 V19 C3 0.80 0.40 0.41 0.62 0.41 0.62 1 2 0.41 0.45 0.48 0.64 0.65 0.57 0.38 3
C18 C12 C16 0.78 0.57 0.79 0.66 0.74 0.58 5 3 0.43 0.39 0.79 0.68 0.82 0.72 0.37 8
C19 C17 C14 0.76 0.49 0.64 0.64 0.57 0.59 3 3 0.38 0.37 0.66 0.65 0.74 0.65 0.32 6
C20 C18 C19 0.76 0.59 0.82 0.74 0.72 0.65 8 6 0.37 0.32 0.81 0.73 0.86 0.74 0.30 14
C21 0 0 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0
C22 0 0 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0
C23 0 0 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0
$cor
V2 C13 C15 C20
V2 1.00 0.24 0.19 0.38
C13 0.24 1.00 0.40 0.62
C15 0.19 0.40 1.00 0.55
C20 0.38 0.62 0.55 1.00
$alpha
V2 C13 C15 C20
1.00 0.90 0.79 0.86
$size
V2 C13 C15 C20
1 5 4 14
#ICLUST - a function to form homogeneous item composites
# based upon Revelle, W. (1979). Hierarchical cluster analysis and the internal structure of tests. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 14, 57-74.
#
# psudo code
# find similarity matrix
# original is either covariance or correlation
# corrected is disattenuated
#find most similar pair
#if size of pair > min size, apply beta criterion
# if beta new > min(beta 1, beta 2) combine pair
#update similarity matrix
#repeat until finished
#then report various summary statistics
#example code
#r.mat<- Harman74.cor$cov
# print(ICLUST(r.mat),digits=2)
#ICLUST is the main function and calls other routines
"ICLUST" <-
function (r.mat,nclusters=1,alpha=3,beta=1,beta.size=4,alpha.size=3,correct=TRUE,reverse=TRUE,beta.min=.5,output=1,digits=2,labels=NULL,cut=0,n.iterations=0,title="ICLUST") {#should allow for raw data, correlation or covariances
#ICLUST.options <- list(n.clus=1,alpha=3,beta=2,beta.size=4,alpha.size=3,correct=TRUE,reverse=TRUE,beta.min=.5,output=1,digits=2)
ICLUST.options <- list(n.clus=nclusters,alpha=alpha,beta=beta,beta.size=beta.size,alpha.size=alpha.size,correct=correct,reverse=reverse,beta.min=beta.min,output=output,digits=digits)
if(dim(r.mat)[1]!=dim(r.mat)[2]) {r.mat <- cor(r.mat,use="pairwise") } #cluster correlation matrices, find correlations if not square matrix
iclust.results <- ICLUST.cluster(r.mat,ICLUST.options)
loading <- cluster.loadings(iclust.results$clusters,r.mat,digits=digits)
fits <- cluster.fit(r.mat,loading$loadings,iclust.results$clusters,digits=digits)
sorted <- ICLUST.sort(ic.load=loading$loadings,labels=labels,cut=cut) #sort the loadings
#now, iterate the cluster solution to clean it up (if desired)
clusters <- iclust.results$clusters
old.clusters <- clusters
old.fit <- fits$clusterfit
clusters <- factor2cluster(loading$loadings,cut=cut,loading=FALSE)
load <- cluster.loadings(clusters,r.mat,digits=digits)
if (n.iterations > 0) { #it is possible to iterate the solution to perhaps improve it
for (steps in 1:n.iterations) { #
load <- cluster.loadings(clusters,r.mat,digits=digits)
clusters <- factor2cluster(loading$loadings,cut=cut,loading=FALSE)
if(dim(clusters)[2]!=dim(old.clusters)[2]) {change <- 999
load <- cluster.loadings(clusters,r.mat,digits=digits) } else {
change <- sum(abs(clusters)-abs(old.clusters)) } #how many items are changing?
fit <- cluster.fit(r.mat,loading$loadings,clusters,digits=digits)
old.clusters <- clusters
print(paste("iterations ",steps," change in clusters ", change, "current fit " , fit$clusterfit))
if ((abs(change) < 1) | (fit$clusterfit <= old.fit)) {break} #stop iterating if it gets worse or there is no change in cluster definitions
old.fit <- fit$cluster.fit
}
}
p.fit <- cluster.fit(r.mat,loading$loadings,clusters,digits=digits)
p.sorted <- ICLUST.sort(ic.load=loading$loadings,labels=labels,cut=cut)
purified <- cluster.cor(clusters,r.mat,digits=digits)
list(title=title,clusters=iclust.results$clusters,corrected=loading$corrected,loadings=loading$loadings,fit=fits,results=iclust.results$results,cor=loading$cor,alpha=loading$alpha,size=loading$size,sorted=sorted,p.fit = p.fit,p.sorted = p.sorted,purified=purified)
}
"ICLUST.sort"<- function (ic.load,cut=0,labels=NULL,loading=FALSE) {
nclust <- dim(ic.load)[2]
nitems <- dim(ic.load)[1]
if (length(labels)==0) {
var.labels <- rownames(ic.load)} else {var.labels=labels}
if (length(var.labels)==0) {var.labels =paste('V',seq(1:nitems),sep='')} #unlabled variables
if(loading) {loadings <- ic.load$loadings} else {loadings <- ic.load}
loads <- data.frame(item=seq(1:nitems),content=var.labels,cluster=rep(0,nitems),loadings)
#first find the maximum for each row and assign it to that cluster
loads$cluster <- apply(abs(loadings),1,which.max)
for (i in 1:nitems) {if (abs(loadings[i,loads$cluster[i]]) < cut) {loading$cluster[i] <- nclust+1}} #assign the ones that missed the cut a location
ord <- sort(loads$cluster,index.return=TRUE)
loads[1:nitems,] <- loads[ord$ix,]
rownames(loads)[1:nitems] <- rownames(loads)[ord$ix]
items <- c(table(loads$cluster),1) #how many items are in each cluster?
if(length(items) < (nclust+1)) {items <- rep(0,(nclust+1)) #this is a rare case where some clusters don't have anything in them
for (i in 1:nclust+1) {items[i] <- sum(loads$cluster==i) } }
#now sort the loadings that have their highest loading on each cluster
first <- 1
for (i in 1:nclust) {
if(items[i]>0 ) {
last <- first + items[i]- 1
ord <- sort(abs(loads[first:last,i+3]),decreasing=TRUE,index.return=TRUE)
loads[first:last,] <- loads[ord$ix+first-1,]
rownames(loads)[first:last] <- rownames(loads)[ord$ix+first-1]
first <- first + items[i]}
}
if (first < nitems) loads[first:nitems,"cluster"] <- 0 #assign items less than cut to 0
ICLUST.sort <- list(sorted=loads) }
ICLUST.cluster <- function (r.mat,ICLUST.options) {#should allow for raw data, correlation or covariances
#options: alpha =1 (minimum alpha) 2 (average alpha) 3 (maximum alpha)
# beta =1 (minimum beta) 2 (average beta) 3 (maximum beta)
# correct for reliability
# reverse score items if negative correlations
# stop clustering if beta for new clusters < beta.min
# output =1 (short) 2 (show steps) 3 show rejects as we go
#initialize various arrays and get ready for the first pass
output <- ICLUST.options$output
num.var <- nrow(r.mat)
keep.clustering <- TRUE #used to determine when we are finished clustering
results <- data.frame(matrix(rep(0,18*(num.var-1)),ncol=18))
names(results) <- c("Item/Cluster", "Item/Cluster","similarity","correlation","alpha1","alpha2",
"beta1","beta2","size1","size2","rbar1","rbar2","r1","r2","alpha","beta","rbar","size")
rownames(results) <- paste("C",1:(num.var-1),sep="")
clusters <- diag(1,nrow =nrow(r.mat)) #original cluster structure is 1 item clusters
rownames(clusters) <- rownames(r.mat)
colnames(clusters) <- paste("V",1:num.var,sep="")
count=1
#master loop
while (keep.clustering) { #loop until we figure out we should stop
#find similiarities
#we will do most of the work on a copy of the r.mat
cluster.stats <- cluster.cor(clusters,r.mat,FALSE)
sim.mat <- cluster.stats$cor #the correlation matrix
diag(sim.mat) <- 0 #we don't want 1's on the diagonal to mess up the maximum
#two ways to estimate reliability -- for 1 item clusters, max correlation, for >1, alpha
#this use of initial max should be an option
if (ICLUST.options$correct) { #find the largest and smallest similarities for each variable
row.range <- apply(sim.mat,1,range,na.rm=TRUE)
row.max <- pmax(abs(row.range[1,]),abs(row.range[2,])) #find the largest absolute similarity
} else {row.max <- rep(1, nrow(sim)) } #don't correct for largest similarity
item.rel <- cluster.stats$alpha
for (i in 1: length(item.rel)) { if (cluster.stats$size[i]<2) {
item.rel[i] <- row.max[i]
#figure out item betas here?
}}
sq.max <- diag(1/sqrt(item.rel)) #used to correct for reliabilities
#this is the corrected for maximum r similarities
if (ICLUST.options$correct) {sim <- sq.max %*% sim.mat %*% sq.max
} else {sim <- sim.mat}
diag(sim) <- NA #we need to not consider the diagonal when looking for maxima
#find the most similar pair and apply tests if we should combine
test.alpha <- FALSE
test.beta <- FALSE
while(!(test.alpha&test.beta)){
max.cell <- which.max(sim) #global maximum
if (length(max.cell) < 1) {
keep.clustering <- FALSE
break} #there are no non-NA values left
sign.max <- 1
if ( ICLUST.options$reverse ) { #normal case is to reflect if necessary
min.cell <- which.min(sim) #location of global minimum
if (sim[max.cell] < abs(sim[min.cell] )) {
sign.max <- -1
max.cell <- min.cell }
if (sim[max.cell] < 0.0) {sign.max <- -1 }}
#this is a weird case where all the similarities are negative
max.col <- trunc(max.cell/nrow(sim))+1 #is in which row and column?
max.row <- max.cell - (max.col-1)*nrow(sim) #need to fix the case of first column
if (max.row < 1) {max.row <- nrow(sim)
max.col <- max.col-1 }
#combine these two rows if the various criterion are passed
beta.combined <- 2* sign.max*sim.mat[max.cell]/(1+sign.max* sim.mat[max.cell]) #unweighted beta
size1 <- cluster.stats$size[max.row]
if(size1 < 2) {V1 <- 1
beta1 <- item.rel[max.row]
alpha1 <- item.rel[max.row]
rbar1 <- item.rel[max.row] } else {
rbar1 <- results[cluster.names[max.row],"rbar"]
beta1 <- results[cluster.names[max.row],"beta"]
alpha1 <- results[cluster.names[max.row],"alpha"]}
V1 <- size1 + size1*(size1-1) * rbar1
size2 <- cluster.stats$size[max.col]
if(size2 < 2) {V2 <- 1
beta2 <- item.rel[max.col]
alpha2 <- item.rel[max.col]
rbar2 <- item.rel[max.col] } else {
rbar2 <- results[cluster.names[max.col],"rbar"]
beta2 <- results[cluster.names[max.col],"beta"]
alpha2 <- results[cluster.names[max.col],"alpha"]}
V2 <- size2 + size2 * (size2-1) * rbar2
Cov12 <- sign.max* sim.mat[max.cell] * sqrt(V1*V2)
V12 <- V1 + V2 + 2 * Cov12
size12 <- size1 + size2
alpha <- (V12 - size12)*(size12/(size12-1))/V12
rbar <- alpha/(size12-alpha*(size12-1))
#what is the correlation of this new cluster with the two subclusters?
#this considers item overlap problems
c1 <- sign.max*rbar1*size1*size1 + sign.max* Cov12 #corrects for item overlap
c2 <- rbar2*size2*size2 + Cov12 #only flip one of the two correlations with the combined cluster
if(size1 > size2) {r1 <- c1/sqrt(V1*V12)
r2 <- sign.max* c2/sqrt(V2*V12) } else {r1 <-sign.max* c1/sqrt(V1*V12)
#flip the smaller of the two clusters
r2 <- c2/sqrt(V2*V12) }
#test if we should combine these two clusters
#first, does alpha increase?
test.alpha <- TRUE
if (ICLUST.options$alpha.size < min(size1,size2)) {
switch(ICLUST.options$alpha, {if (alpha < min(alpha1,alpha2)) {if (output>2) {print(
paste ('do not combine ', cluster.names[max.row],"with", cluster.names[max.col],
'new alpha =', round (alpha,2),'old alpha1 =',round( alpha1,2),"old alpha2 =",round(alpha2,2)))}
test.alpha <- FALSE }},
{if (alpha < mean(alpha1,alpha2)) {if (output>2) {print(paste ('do not combine ',
cluster.names[max.row],"with", cluster.names[max.col],'new alpha =', round (alpha,2),
'old alpha1 =',round( alpha1,2),"old alpha2 =",round(alpha2,2)))}
test.alpha <- FALSE }},
{if (alpha < max(alpha1,alpha2)) {if (output>2) {print(paste ('do not combine ',
cluster.names[max.row],"with", cluster.names[max.col],'new alpha =', round (alpha,2),
'old alpha1 =',round( alpha1,2),"old alpha2 =",round(alpha2,2)))}
test.alpha <- FALSE }}) #end switch
} #end if options$alpha.size
#second, does beta increase ?
test.beta <- TRUE
if (ICLUST.options$beta.size < min(size1,size2)) {
switch(ICLUST.options$beta, {if (beta.combined < min(beta1,beta2)) {if (output>2) {print(
paste ('do not combine ', cluster.names[max.row],"with", cluster.names[max.col],'new beta =',
round (beta.combined,2),'old beta1 =',round( beta1,2),"old beta2 =",round(beta2,2)))}
test.beta <- FALSE }},
{if (beta.combined < mean(beta1,beta2)) {if (output>2) {print(paste ('do not combine ',
cluster.names[max.row],"with", cluster.names[max.col],'new beta =', round (beta.combined,2),
'old beta1 =',round( beta1,2),"old beta2 =",round(beta2,2)))}
test.beta <- FALSE }},
{if (beta.combined < max(beta1,beta2)) {if (output>2) {print(paste ('do not combine ',
cluster.names[max.row],"with", cluster.names[max.col],'new beta =', round (beta.combined,2),
'old beta1 =',round( beta1,2),"old beta2 =",round(beta2,2)))}
test.beta <- FALSE }}) #end switch
} #end if options$beta.size
if(test.beta&test.alpha) {break } else {
if (beta.combined < ICLUST.options$beta.min) {
keep.clustering <- FALSE #the most similiar pair is not very similar, we should quit
break} else {sim[max.row,max.col] <- NA
sim[max.col,max.row] <- NA }
} #end of test.beta&test.alpha
} #end of while test.alpha&test.beta.loop
#combine and summarize
if (keep.clustering)
{ # we have based the alpha and beta tests, now combine these two variables
clusters[,max.row] <- clusters[,max.row] + sign.max * clusters[,max.col]
cluster.names <- colnames(clusters)
#summarize the results
results[count,1] <- cluster.names[max.row]
results[count,2] <- cluster.names[max.col]
results[count,"similarity"] <- sim[max.cell]
results[count,"correlation"] <- sim.mat[max.cell]
results[count,"alpha1"] <- item.rel[max.row]
results[count,"alpha2"] <- item.rel[max.col]
size1 <- cluster.stats$size[max.row]
size2 <- cluster.stats$size[max.col]
results[count,"size1"] <- size1
results[count,"size2"] <- size2
results[count,"beta1"] <- beta1
results[count,"beta2"] <- beta2
results[count,"rbar1"] <- rbar1
results[count,"rbar2"] <- rbar2
results[count,"r1"] <- r1
results[count,"r2"] <- r2
results[count,"beta"] <- beta.combined
results[count,'alpha'] <- alpha
results[count,'rbar'] <- rbar
results[count,"size"] <- size12
results[count,3:18] <- round(results[count,3:18],ICLUST.options$digits)
#update
cluster.names[max.row] <- paste("C",count,sep="")
colnames(clusters) <- cluster.names
clusters <- clusters[,-max.col]
cluster.names<- colnames(clusters)
#row.max <- row.max[-max.col]
} #end of combine section
if(output > 1) print(results[count,],digits=2)
count=count+1
if ((num.var - count) < ICLUST.options$n.clus) {keep.clustering <- FALSE}
if(num.var - count < 1) {keep.clustering <- FALSE} #only one cluster left
} #end of keep clustering loop
ICLUST.cluster <- list(results=results,clusters=clusters,number <- num.var - count)
} # end ICLUST.cluster
cluster.loadings <-
function (keys, r.mat, correct = TRUE,digits=2)
{
if (!is.matrix(keys))
keys <- as.matrix(keys)
item.covar <- r.mat %*% keys #item by cluster covariances
covar <- t(keys) %*% item.covar #variance/covariance of clusters
var <- diag(covar)
sd.inv <- 1/sqrt(var)
key.count <- diag(t(keys) %*% keys) #how many items in each cluster?
if (correct) {
cluster.correct <- diag((key.count/(key.count - 1)))
for (i in 1:ncol(keys)) {
if (key.count[i]==1) { #fix the case of 1 item keys
cluster.correct[i,i] <- 1
} else { cluster.correct[i,i] <- key.count[i]/(key.count[i]-1)
item.covar[,i] <- item.covar[,i] - keys[,i]}
} #i loop
correction.factor <- keys %*% cluster.correct
correction.factor[ correction.factor < 1] <- 1
item.covar <- item.covar * correction.factor
}
ident.sd <- diag(sd.inv, ncol = length(sd.inv))
cluster.loading <- item.covar %*% ident.sd
cluster.correl <- ident.sd %*% covar %*% ident.sd
key.alpha <- ((var - key.count)/var) * (key.count/(key.count - 1))
key.alpha[is.nan(key.alpha)] <- 1
key.alpha[!is.finite(key.alpha)] <- 1
colnames(cluster.loading) <- colnames(keys)
colnames(cluster.correl) <- colnames(keys)
rownames(cluster.correl) <- colnames(keys)
rownames(cluster.loading) <- rownames(r.mat)
if( ncol(keys) >1) {cluster.corrected <- correct.cor(cluster.correl, t(key.alpha))} else {cluster.corrected <- cluster.correl}
return(list(loadings=round(cluster.loading,digits), cor=round(cluster.correl,digits),corrected=round(cluster.corrected,digits), sd = round(sqrt(var),digits), alpha = round(key.alpha,digits),
size = key.count))
}
cluster.fit <- function(original,load,clusters,diagonal=FALSE,digits=2) {
sqoriginal <- original*original #squared correlations
totaloriginal <- sum(sqoriginal) - diagonal*sum(diag(sqoriginal) ) #sum of squared correlations - the diagonal
load <- as.matrix(load)
clusters <- as.matrix(clusters)
model <- load %*% t(load) #reproduce the correlation matrix by the factor law R= FF'
residual <- original-model #find the residual R* = R - FF'
sqresid <- residual*residual #square the residuals
totalresid <- sum(sqresid)- diagonal * sum(diag(sqresid) ) #sum squared residuals - the main diagonal
fit <- 1-totalresid/totaloriginal #fit is 1-sumsquared residuals/sumsquared original (of off diagonal elements
clusters <- abs(clusters)
model.1 <- (load * clusters) %*% t(load*clusters)
residual <- original - model.1
sqresid <- residual*residual #square the residuals
totalresid <- sum(sqresid)- diagonal * sum(diag(sqresid) ) #sum squared residuals - the main diagonal
fit.1 <- 1-totalresid/totaloriginal #fit is 1-sumsquared residuals/sumsquared original (of off diagonal elements
cluster.fit <- list(clusterfit=round(fit.1,digits),factorfit=round(fit,digits))
}